Even the most attentive driver can miss a sign or signal on the road. Do so at the wrong place (and with the wrong person watching), and you could end up with a ticket for violating CVC 21461 (failure to obey traffic signals).
So what do you do next? While this ticket can come with fines, points, and other consequences, there are some steps you can take to defend yourself — and keep your driving record clean. Read on to learn everything you need to know about CV 21461, including the consequences of a violation, how to fight it in court, and more.
What is a CVC 21461: Failure to Obey Traffic Signals?

CVC 21461 is a California Vehicle Code section that pertains to the failure to obey traffic signals. Specifically, it states that a driver must obey traffic signals, devices, and traffic control signals, unless otherwise directed by a police officer.
Here’s the full text of the law:
“21461a VC It is unlawful for a driver of a vehicle to fail to obey a sign or signal defined as regulatory in the federal Manual on Uniform Traffic Control Devices, or a Department of Transportation approved supplement to that manual of a regulatory nature erected or maintained to enhance traffic safety and operations or to indicate and carry out the provisions of this code or a local traffic ordinance or resolution adopted pursuant to a local traffic ordinance, or to fail to obey a device erected or maintained by lawful authority of a public body or official.”
Traffic school can help you keep a clean driving record, prevent insurance increases, and more!
CVC 21461 Violations
Violating CVC 21461 may be easier than you think. This is a broad traffic law that encompasses many different actions and scenarios that drivers encounter all the time, making it easier to break the law — even unintentionally.
Types of CVC 21461a VC Violations
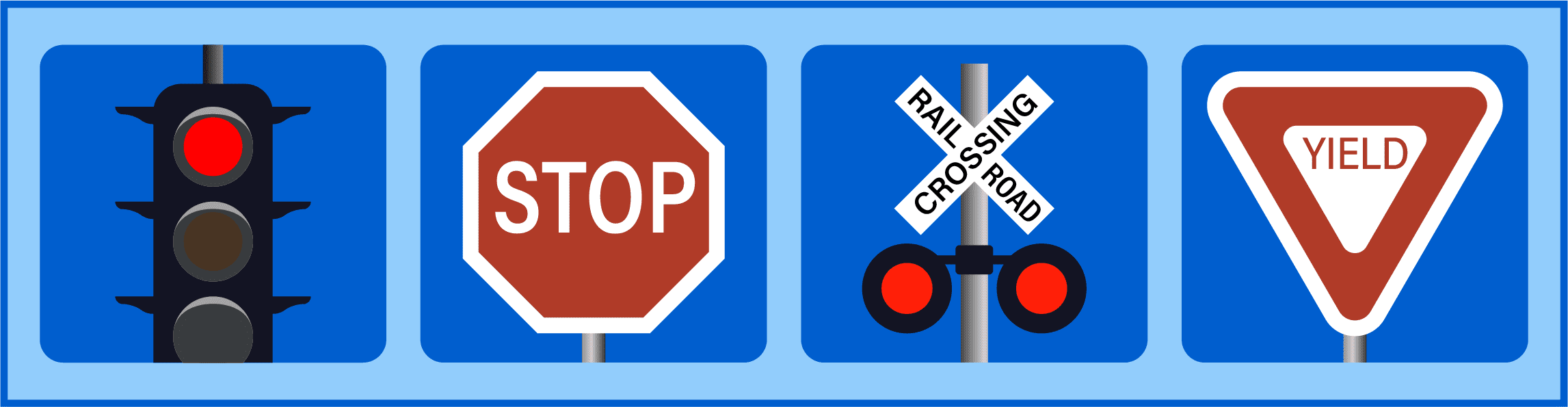
There are many actions that could result in a CVC 21461 ticket. A few examples include:
- Running a red light. If a driver enters an intersection after the traffic signal has turned red, they have violated CVC 21461. If they are caught by camera, this can result in a a red camera light ticket.
- Ignoring a stop sign. If a driver fails to come to a complete stop at a stop sign, they are in violation of CVC 21461.
- Disobeying a yield sign. If a driver fails to yield to other vehicles or pedestrians as required by a yield sign, they risk getting a CVC 21461 ticket.
- Ignoring a railroad crossing signal. If a driver fails to stop at a railroad crossing when the signal indicates that a train is approaching, they are in violation of CVC 21461.
Essentially, any time you take an action while driving that does not follow the signs and signals on the road, you risk a CVC 21461 violation.
Even if you disobey a traffic signal unintentionally (for example, because you didn’t see it), you could be cited for CVC 21461. The California Vehicle Code puts the onus on drivers to be aware of their surroundings at all times so they don’t miss any signs or signals on the road.
Read: California Road Signs and Their Meanings
What Are the Consequences of a CVC 21461 Violation?
The consequences of a CVC 21461 violation depend on several factors, including the specific circumstances of the violation and the driver’s previous driving record. Here are some potential consequences of a CVC 21461 violation.
Fines and fees
The base fine for a CVC 21461 violation is $238. Additional court and administration fees depend on the country where you received the ticket.
Points on your driver’s license.
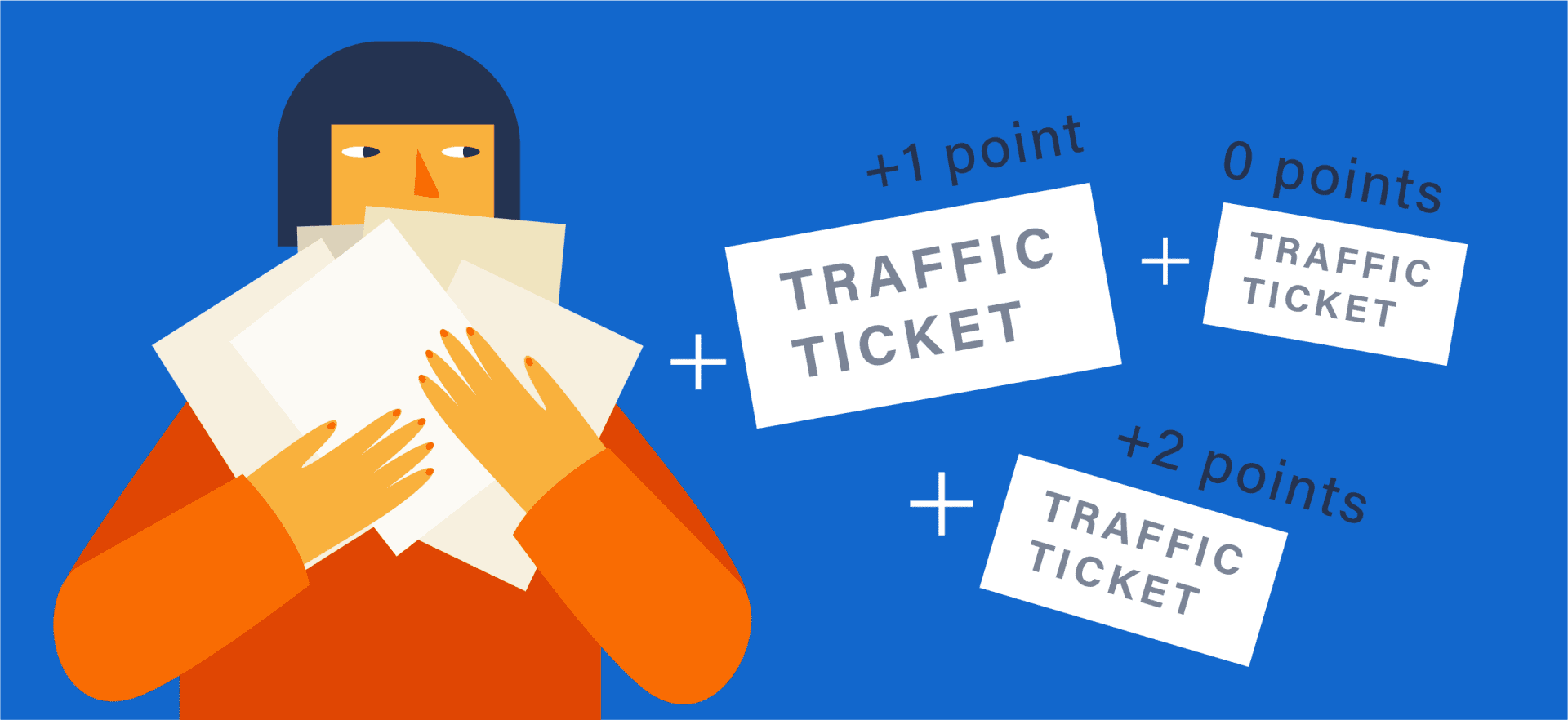
The Negligent Operator Treatment System (NOTS) is a point-based system used by the California Department of Motor Vehicles (DMV) to identify and take action against drivers who accumulate too many points on their driving record. The NOTS system is designed to identify and re-educate drivers who repeatedly violate traffic laws or exhibit other unsafe driving behaviors.
Under the NOTS system, a driver will receive points on their driving record for each traffic violation they commit. The number of points depends on the severity of the violation. For example, a CVC 21461 violation for failing to obey traffic signals will result in one point on the driver’s record. More serious violations, such as driving under the influence (DUI), can result in two or more points.
If a driver accumulates too many points within a specific period, the DMV may take action against their driving privileges. Here are the consequences for accumulating points under the NOTS system:
| Action | Given when you accumulate… |
| Level 1: Warning letter | 2 points within 12 months 4 points within 24 months 6 points within 36 months |
| Level 2: Notice of intent to suspend Note: Before the suspension happens, you can defend yourself by requesting a hearing. Typically, this needs to be done within two weeks of receiving the notice. | 3 points within 12 months 5 points within 24 months 7 points within 36 months You may also get this notice if a major conviction is added to your driving record. |
| Level 3: Order of probation/suspension Note: Probation lasts for one year, and suspension of your driver’s license lasts for six months. The action is effective 34 days from when the order is mailed to you. | 4 points within 12 months 6 points within 24 months 8 points within 36 months |
| Level 4: Violation of NOTS probation | Any violation or crash that occurs while your license is suspended. Any one- or two-point conviction during your probation period. Any failure to appear or failure to pay fines and fees during your probation period. Any driver under the age of 18 who violates their provisional probation because of an at-fault collision, failure to appear, failure to pay, or other offense. |
Increased insurance rates.
A CVC 21461 violation is considered a moving violation, and it may result in increased insurance rates.
How Much Does a CVC 21461 Cost?
The base fine for a CVC 21461 is $238.
It’s important to note that this is just the base fine, and additional fees and penalties may apply. For example, if the violation occurred in a construction zone or a school zone, the fine may be higher. There will also be additional court and administrative fees that vary based on the county where the violation occurred. These can easily push the cost of the ticket over $500.
But the fines are just the beginning of the cost of a CVC 21461 ticket.
Getting even a single point on your California driver’s license can cause your insurance rates to increase — though the amount of your increase depends on your insurance carrier and many individual factors. An analysis by The Zebra found that a single CVC 21461 ticket can cause insurance rates to increase by over 22%, or an average premium increase of more than $330.
Can You Go to Traffic School for CVC 21461?
Yes, in most cases, a driver who receives a CVC 21461 violation can attend traffic school.
There are a few benefits to attending traffic school for a CVC 21461 violation:
- Masking the point from your license. Attending traffic school can mask one point from your license. Note that this doesn’t remove it from your driving record, but it prevents insurance companies from being able to see it, which means your rates will not increase because of the CVC 21461 ticket.
- Education and better driving skills. Traffic school can provide drivers with education and skills to help them become safer and more responsible drivers. This can help prevent future violations and improve your overall driving performance.
If you do decide to attend traffic school, why not do it in the most convenient, affordable way possible — through Best Online Traffic School?
Our traffic school course is fully licensed by the California DMV in all counties. It’s fully online and can be completed on your own time, on any internet-connected device. And our course is one of the most affordable ones out there — plus, you don’t have to pay a penny until you pass the final quiz and you’re ready to send your results to the DMV.
Traffic school can help you save on insurance after you get a ticket — start for free today.
How To Fight a CVC 21461 Violation
If you receive a CVC 21461 violation in California, you may be able to fight it in court. Here are some steps you can take to fight the violation.
- Plead not guilty. There should be instructions on the back of your ticket that tell you exactly how to do this, along with contact information for your court. Note that even though you’re pleading not guilty, you’ll still need to pay the fine for the ticket as bail. This will be refunded to you if you win your case and are found not guilty.
- Understand the violation. It’s important to understand the specifics of the CVC 21461 violation, including the circumstances surrounding your alleged violation, the location and condition of the traffic signal or sign, and any other relevant factors. This can help you determine whether the violation was justified or whether there are potential legal defenses.
- Gather evidence. Collect any evidence that supports your case, including any photos, videos, witness statements, or other documentation. This evidence can help demonstrate that the violation was unwarranted or that the traffic signal or sign was not visible or functioning correctly.
- Present your case. In court, present your case clearly and concisely, providing any evidence or testimony that supports your position. Be respectful and professional throughout the proceedings.
- Consider alternatives. If you are unable to successfully fight the CVC 21461 violation in court, you may want to consider asking to attend traffic school or negotiating a plea deal to minimize the penalties and consequences.
Rather than going to court, you may also be able to fight the ticket using trial by written declaration.
How to Write a Trial by Written Declaration for Failure to Obey Traffic Signals
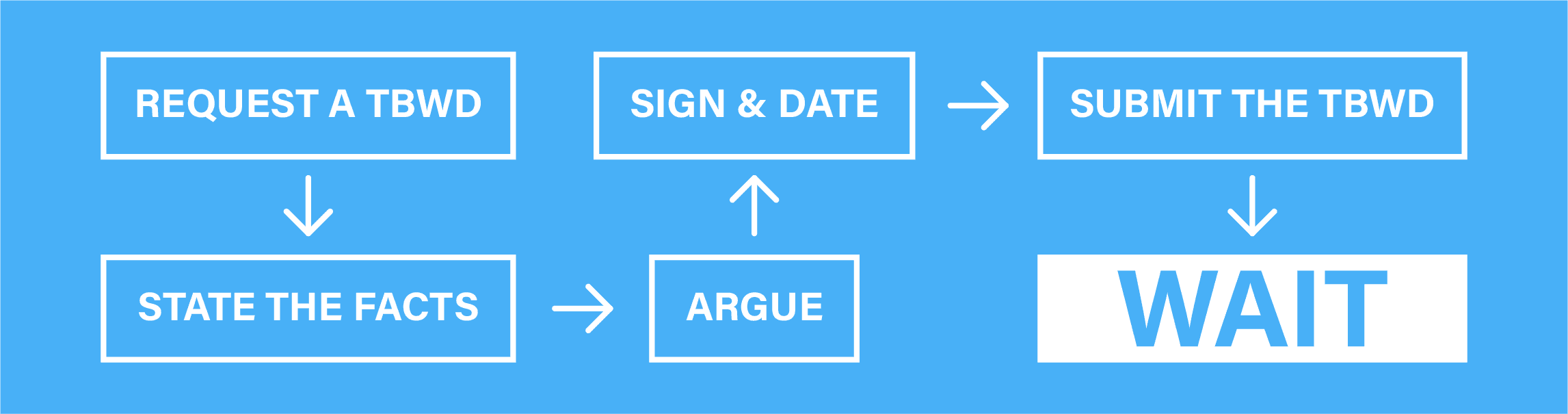
A Trial by Written Declaration (TBWD) is a legal process that allows a driver to contest a traffic ticket without having to appear in court. Here’s what to do to write a TBWD for Failure to Obey Traffic Signals (CVC 21461) in California.
- Request a TBWD. Your request must be made within 45 days of receiving the ticket.
- State the facts. In your written declaration, provide a detailed and factual explanation of the events leading up to the alleged violation. Explain why you believe you did not violate CVC 21461. You can include any evidence, like photos or videos, that supports your version of events.
- Argue your case. Provide a legal argument supporting your position. Explain why the citation was not warranted and why the evidence supports your innocence. You can reference the California Vehicle Code or other relevant laws to support your argument.
- Sign and date. Sign and date your written declaration and include a statement that you declare under penalty of perjury that the information provided is true and correct.
- Submit the TBWD. Submit your written declaration to the court by mail or in person before the deadline specified by the court. The officer who issued your ticket will also submit their own written declaration so the judge can review both sides of the case.
- Wait for the verdict. After reviewing your TBWD, the court will issue a verdict either finding you guilty or not guilty. If found guilty, you have the option to appeal by requesting a trial de novo, which is a new trial in front of a judge.
Should I Hire a Lawyer for a CVC 21461?
Whether you should hire a lawyer for a CVC 21461 violation is a personal choice. There are many different factors you should take into consideration when deciding whether to hire legal representation after getting any traffic ticket.
First, consider the severity of the violation. If the CVC 21461 violation is relatively minor, such as running a red light, and there is little evidence against you, you may be able to handle the case on your own. However, if the violation is more serious, such as causing an accident or injury, or if you have a history of traffic violations, it may be advisable to hire a lawyer.
You should also consider the potential consequences of being found guilty. If you are at risk of losing your driver’s license or facing other serious consequences, hiring a lawyer may be a good idea.
Next, consider your own legal knowledge. If you are not familiar with the legal system or are unsure about how to contest a traffic violation, hiring a lawyer can be helpful. A lawyer can provide guidance on the best course of action and help you navigate the legal process.
And finally, consider the cost-benefit analysis. Hiring a lawyer can be expensive, but it may be worth the investment if it can help you avoid more significant consequences or if you have a strong case that can potentially result in a dismissal or reduction of the charges. (Learn more about the cost/benefit of hiring a traffic lawyer in How Much Does a Traffic Lawyer Cost?)
After all these considerations, if you are still unsure about whether to hire a lawyer, consider scheduling an initial consultation with one to discuss your options.
CVC 21461: What to Do Next
Getting any type of traffic ticket can be a stressful experience — and that includes a CVC 21461 violation. Before you take the next step, know all your options, and consider traffic school as one of the most cost-effective ways to reduce the long-term effects of getting a ticket.