If you ever consume alcohol, you should know about blood alcohol content or BAC. Used to measure the amount of alcohol in a person’s blood, BAC is used for both health and legal purposes in a variety of different scenarios. Before you crack open your next adult beverage, take the time to read up on blood alcohol content — here’s everything you need to know.
What is Blood Alcohol Content (BAC)?
Blood alcohol content, also called blood alcohol level or BAC, is a measure of the amount of alcohol a person has in their blood.
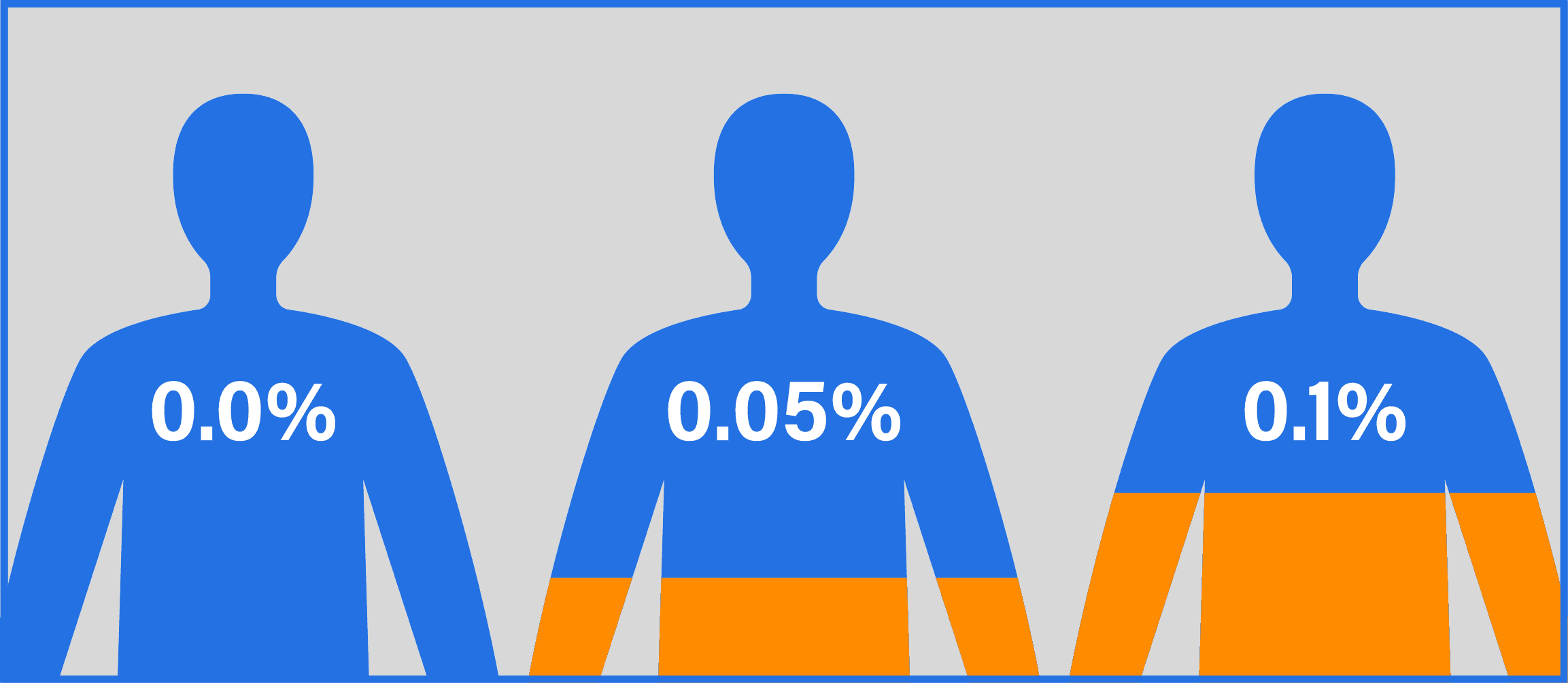
It’s displayed as a percentage, ranging from 0.0% (no alcohol) to 0.4% or higher (a dangerous level of intoxication). BAC is calculated in grams of alcohol per 100 mL of blood, which means a .08% BAC (the legal limit to drive a vehicle in the U.S.) would mean blood that is 0.08% alcohol by volume.
Alcohol (also known as ethyl alcohol or ethanol) is an ingredient in beer, wine, and liquor that causes intoxication. When you drink an alcoholic beverage, the alcohol is absorbed by your stomach and intestines into your bloodstream. The alcohol is later filtered out of the blood by your liver.
If you consume alcoholic beverages faster than your liver can remove the alcohol from your blood, your BAC will increase. This causes drunkenness. How fast your liver can process alcohol and remove it from your body depends on many factors, including your age, body weight, sex, and whether there was food in your stomach when you drank the alcohol.
Traffic school can help you keep a clean driving record, prevent insurance increases, and more!
How Are Blood Alcohol Levels Measured?
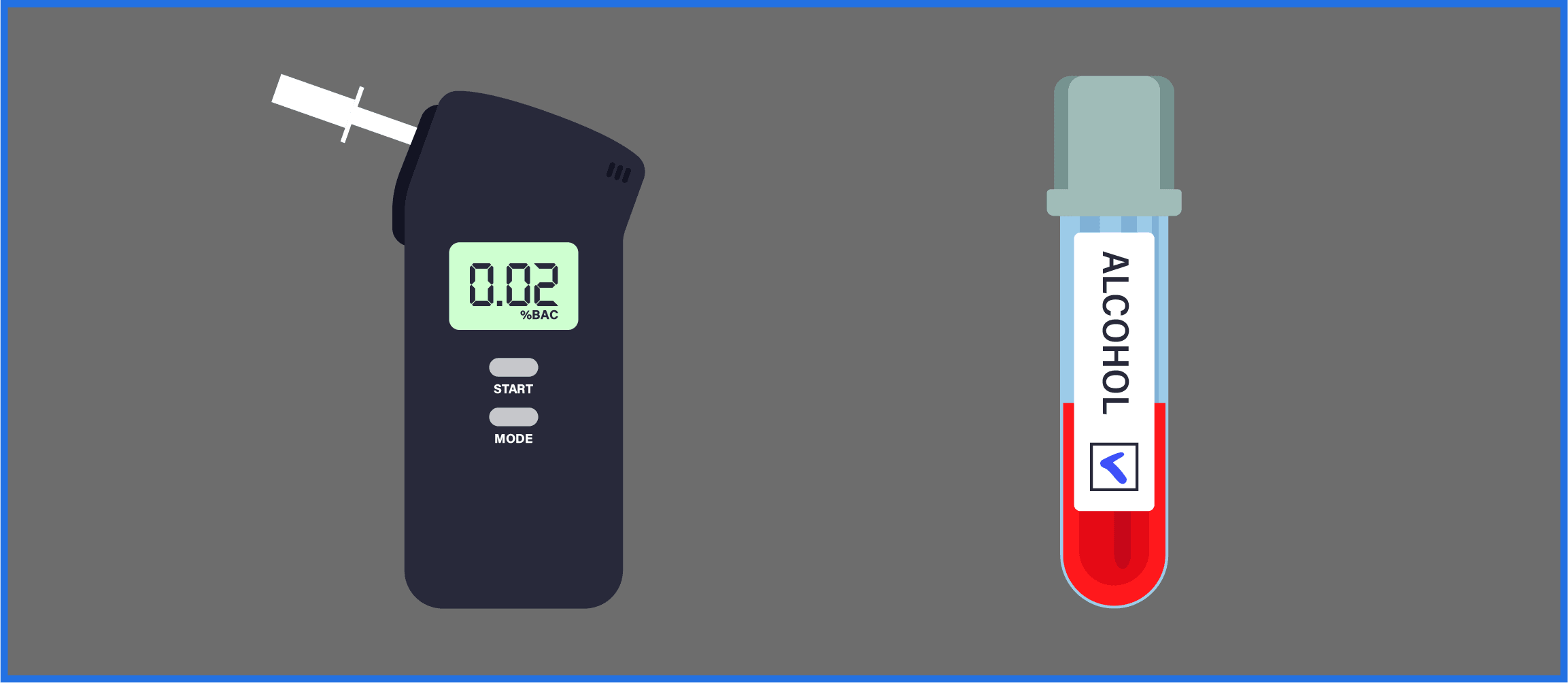
Your blood alcohol level can be measured in one of two ways: Using a breathalyzer, or a blood test.
When a breathalyzer is used, you’ll exhale deeply into a tube connected to a small device that reads how much alcohol is on your breath. BAC is measured as grams of alcohol detected per 210 liters of breath, since the ratio of breath alcohol to blood alcohol is 2,100:1.
A blood test is generally considered to be a more accurate way to measure BAC. With a blood test, a medical or public safety worker will draw a small amount of your blood, then send it to a lab to be analyzed. The lab can pinpoint the alcohol content in the blood sample, which shows your BAC at the time the blood was drawn.
You can use a blood alcohol content calculator online to get a rough idea of your level.
Why Might You Have Your BAC Tested?

People have their Blood Alcohol Content tested for many different reasons, but some of the most common are:
- Medical testing. If you are suspected of having alcohol poisoning, a potentially life threatening condition, medical personnel will administer a BAC test so they can begin treatment as quickly as possible.
- Drinking and driving. If you are pulled over and suspected of drinking and driving, police may request a BAC test to see if you are at or above 0.08% BAC, which is the legal limit for someone 21 or older to drive in the U.S. Drivers who are under 21 years of age are prohibited from driving with any alcohol in their system.
- Other legal purposes. Police may also request a BAC test to determine if someone is drunk in public or breaking any other alcohol-related laws.
- Addiction treatment. Anyone who is in addiction treatment that prohibits alcohol consumption may have their BAC tested at any time.
How Do Different Levels of Blood Alcohol Content Affect You?
Alcohol is a depressant, which means it reduces stimulation in your central nervous system. It also affects you both physically and mentally in a wide variety of ways, depending on how high your BAC gets.
Here are some of the common physical and mental effects of different BAC percentages.
- 0.0% BAC: There is no alcohol in your system, so you are sober.
- 0.02% BAC: You may experience a slightly altered mood, feelings of relaxation, and slightly impaired judgment. To others, you are likely to appear normal up to about this BAC.
- 0.05% BAC: You may begin to feel uninhibited. You may also experience lower levels of alertness and more significantly impaired judgment. To others, you will likely appear talkative and outgoing.
- 0.08% BAC: You may experience reduced muscle coordination, along with significant impairment to judgment, reasoning, and decision-making. Notably, people at this BAC often find it difficult to detect danger. This is the legal limit for people over age 21 to operate a vehicle. If you drive at this BAC or higher, you are at risk of getting a DUI.
- 0.1% BAC: You will likely experience reduced reaction times and significantly slowed thinking. Slurring words is also common at this BAC. To others, you are likely to appear quite drunk at this BAC or higher; you may appear overexuberant or sloppy.
- 0.15% BAC: You will likely experience altered moods, loss of coordination, and difficulty balancing and controlling muscle movements. You may also experience nausea and vomiting.
- 0.15 to 0.3% BAC: You’re likely to be significantly drowsy and confused. Vomiting is extremely common at this level of BAC.
- 0.3 to 0.4% BAC: At this BAC, you are at serious and immediate risk for alcohol poisoning. This level of intoxication can be life-threatening. At this stage, you are likely to experience vomiting and loss of consciousness, and should seek medical care.
- 0.4% BAC and higher: This BAC level is potentially fatal. Coma, respiratory arrest, and death become risks at this BAC.
How Do You Lower Your Blood Alcohol Content?
You might recall from earlier in this article that your BAC only rises if you drink alcohol faster than your body can metabolize and process it. That means that if you stick to just one alcoholic drink per hour or two, your BAC is far less likely to rise (though it still depends on many factors including your size, weight, and whether you ate food prior to drinking).
Once your BAC has risen, however, the only way to bring it down is to wait for your liver to process the alcohol from your bloodstream. Typically, this occurs at a rate of about 0.015% BAC per hour.
There are many old wives’ tales about how someone can sober up more quickly — eating a large or greasy meal, drinking coffee, or taking a cold shower are commonly touted as ways. But these actually have no effect whatsoever on your BAC. The only way to lower your BAC is to stop drinking alcohol and wait for your body to process any you’ve already consumed.
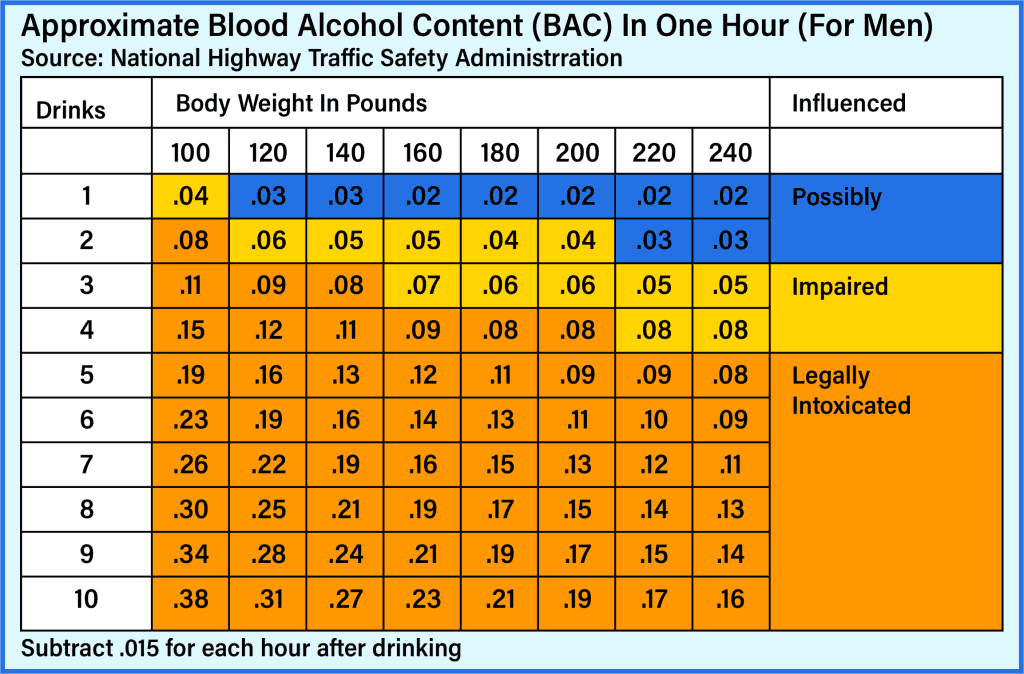
How to Estimate Your Blood Alcohol Content
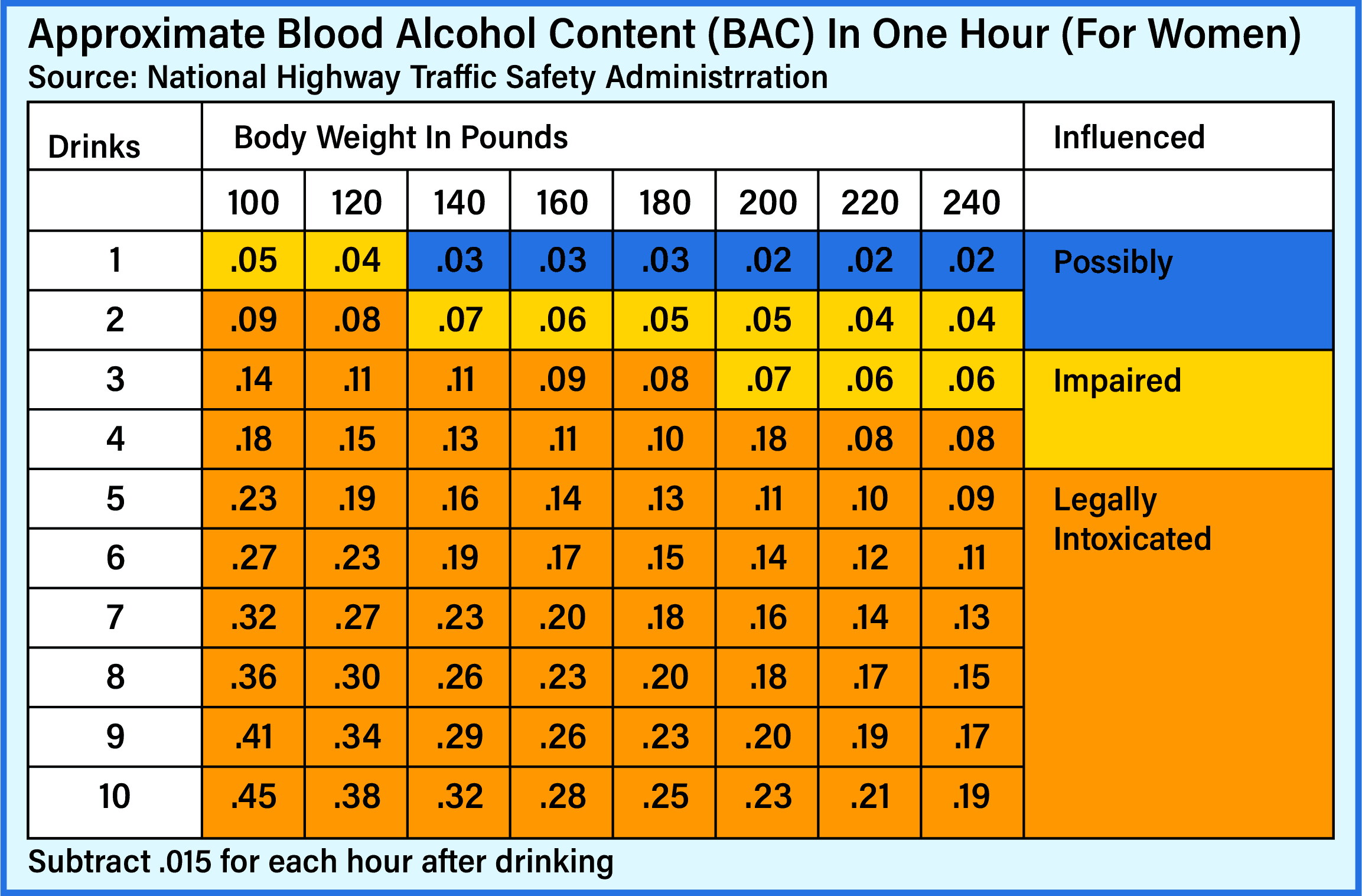
There’s no way to accurately check your BAC without taking a breathalyzer or blood test. However, you can get a rough estimate based on your sex, body weight, and how many alcoholic drinks you’ve consumed over a specific amount of time.
For women:
For men:
It’s also possible to purchase personal breathalyzer devices. Be warned, though, that many of these devices are not qualified medical devices, and the results they show may be inaccurate.
What Impacts Your Blood Alcohol Content?
As we’ve mentioned earlier in this article, not everyone will have the exact same BAC, even after consuming the same amount of alcohol. Your blood alcohol content is impacted by:
- Sex. Men tend to have a lower BAC than women after consuming the same amount of alcohol in the same amount of time.
- Body weight. If you weigh more, alcohol will absorb into your blood more slowly, resulting in a lower BAC.
- How quickly you drink. It may seem obvious, but drinking alcohol very quickly will raise your BAC, since your drinking is likely to outpace the speed at which your body can process the alcohol.
- How much alcohol is in your drinks. Not all alcoholic beverages are made equal. Some drinks, especially cocktails made with mixed liquors or craft beers, can be higher in alcohol content, containing more than one serving of alcohol per drink. Drinking beverages that have a higher alcohol content will result in a higher BAC.
- Whether you ate before drinking. If there’s food in your stomach and intestines, it blocks them from immediately absorbing alcohol into your bloodstream. This means a lower BAC than you would have if you drank on an empty stomach, with nothing to get in the way of the alcohol going right into your blood.
How Alcohol Affects You
Alcohol consumption has many short- and long-term effects beyond BAC.
Consuming alcohol in moderation has not been proven to be extremely dangerous. However, regularly drinking can possibly result in:
- Dehydration
- Intoxication
- Alcoholism (addiction to alcohol)
- Increased risk of certain cancers
- Heart muscle damage
- Stroke
- High blood pressure
- Liver disease
- Accidental injury
- Brain damage
If you consume alcohol, it’s important to talk to your doctor about how often and the amount you drink. They will be able to tell you if you’re at risk for any alcohol-related health problems, or if alcohol might have a negative effect on any existing, unrelated health conditions.
How Blood Alcohol Content Affects Your Driving Ability
Consuming alcohol affects people in many ways that can impact their ability to drive a vehicle. Some of those include:
- Judgment. Alcohol limits your ability to make reasonable judgments, which is a required skill when driving.
- Concentration. Alcohol also affects your ability to concentrate, especially on more than one task at a time. Safe driving requires concentrating while multitasking — you have to pay attention to the road in front of you, your surroundings, your speed, positions of other vehicles, and many other factors.
- Comprehension. Alcohol lowers your comprehension ability, which is required while driving as you need to comprehend and follow signs and signals quickly.
- Motor skills. Alcohol reduces motor skills, which are also necessary for safe driving — you must be able to grip the wheel, judge how far to turn it, and use both the gas and brake pedals.
- Vision and hearing. Alcohol can reduce your visual acuity by up to 32%! Being intoxicated can mean less depth perception and altered ability to perceive distances. This is extremely dangerous while driving, when vision is a critical sense for keeping yourself and other safe on the road.
- Reaction time. Alcohol can slow your reaction time by 15-25%. That means that car crashes that might have been avoidable might happen if you drink and drive.
Read: Drunk Driving Statistics
The Bottom Line: Alcohol and Driving Don’t Mix
If you drink alcohol, it’s important to have a strong understanding of how it affects you and your body and mind. Even if you are below the legal limit, alcohol can impair senses that are necessary for safe driving and make you less safe behind the wheel. Remember to always take steps to protect yourself and others — consider taking a taxi or rideshare, having a designated driver, or just drinking at home where you don’t need to drive.
